QUANTUM RESEARCH LAB
Merging deep learning with quantum advantage for value-based innovations in healthcare

HUMAN-CENTRIC AI
We apply deep learning and leverage quantum advantages when beneficial, driving value-based innovations in healthcare.
No hype, no magic—just maths and physics.
Our technology is crafted by humans for humans with responsibility and care for future generations
RESEARCH & DISCOVERIES
PAST RESEARCH
PROJECT

Preclinical hyperpolarized MRI metabolic biomarkers development
Hyperpolarization provides unprecedent boost in signal to noise ratio (SNR) in MRI allowing metabolic information acquisition keeping great advantages of magnetic resonance modality.
During the project classical machine learning tools were employed to leverage the dataset size.
PAST RESEARCH PROJECT
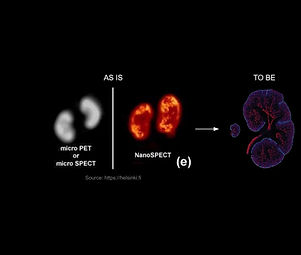
Preclinical bioimaging with higher spatial resolution
Deploying hybrid Neural Networks (QNN+DNN)
in tomographic reconstruction algorithm starting with SPECT molecular imaging modality.
In clinical settings QNN provide opportunities to further boost image quality and allow for lower dose or faster examinations - demanding fewer projections.
CURRENT RESEARCH PROJECT

AI-driven engineering
of superselective nanomedicine
Training Graph Neural Networks (GNN) for latent space embeddings to guide laboratory formulations discovery by prior in-silico prediction of optimal nanoparticle parameters conditioned by energy landscape optimization. The system aims to provide a tool for direct sampling in high-dimensional parameter spaces to maximize specificity and selectivity to the target cells.
CURRENT RESEARCH PROJECT

AI-inhanced Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic Model
Powered by Physics-Informed Neural Networks (PINNs) the model aims to describe in vivo absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion (ADME) of nanoparticles (NP) administered to a model organism. By providing comprehensive prediction of NP biodistribution, it serves a basis for model-guided in-vivo experiment with promising candidate nanoparticles.
PRECLINICAL BIOIMAGING
WITH A HIGHER SPATIAL RESOLUTION
deploying hybrid Neural Networks (QNN+DNN)
in tomographic reconstruction algorithm
starting with SPECT molecular imaging modality

GOAL 1
to empower biomedical and pharma practitioners with fast, low dose and high-resolution scans
for precise evaluation and quantification

THE PROBLEM
Research animals are small
Image resolution matters: with the current SPECT resolution of 0.2-0.4 mm it is still challenging to navigate through mouse brain structures or cancer vs healthy tissue
Dose for radiopharmaceutical matters: high concentration may affect animals and distort experiment results
Future transition to In ovo and Ex ovo studies demands further detalization*

A SOLUTION
Quantum & Classical Neural Networks (QNN + DNN)
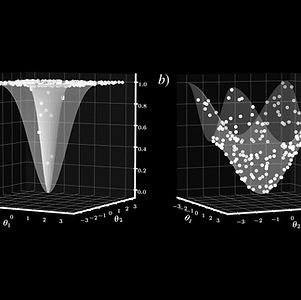
Quantum Neural Networks (QNN) can be trained to lower losses faster, have higher effective dimensions and may require less parameters and data than classical Deep Neural Networks (DNN)*
DNN reconstruction algorithms have already offered imaging with lower noise, higher resolution and contrast**
QNN provide opportunities to further boost image quality. Allowing for lower dose or faster examinations - demanding fewer projections
* DOI 10.1038/s43588-021-00084-1
** DOI: 10.1109/trpms.2020.2994041, 10.1109/TMI.2018.2832613, 10.1109/TMI.2018.2820120
HOW IT WORKS

STEP 1
Raw Data Acquisition:
preclinical lab partnering
study design development

STEP 2
A hybrid QNN+DNN architecture development, training and tuning
STEP 3
Documentation, patent application
PRECLINICAL DEMAND
over 190 mln rodents are used in research and testing annually
on behalf of Pharmaceutical Companies,
Contract Research Organization (CRO’s), Biotech Companies
12-24
million
rodents in the USA
6,5
million
rodents in the EU*
*ALURES
3
times per week maximum scanning
THE FUTURE
Reduction of acquisition Time and Dose in Clinical Molecular Imaging, starting with SPECT
Quantum Neural Networks (QNN) enhance image quality, enabling lower radiation doses and faster examinations with fewer projections required.
This approach meets the increasing demand for more powerful diagnostics across various medical fields, from cardiology to oncology, and addresses challenges in theranostics, dosimetry, and treatment planning.

CLINICAL NEED
SPECT can do more
The current spatial resolution of 2-6 mm is not too high but this technique is affordable and widely available worldwide
Multi-tracer and theranostic potential of the modality require higher signal to noise ratio
Improved image quality makes SPECT a great tool for a robust high precision quantification on existing facilities
TEAM MEMBERS
We have competencies in Medicine, Mathematics, Engineering, and Economics, and are on a mission to create value in the healthcare industry

EVGENY ALEKSANDROV
Radiologist, Specialist in Medical Imaging
CONNECT
Reach out to us for partnership opportunities. Let's discuss how to integrate AI into your research.
PARTNERS
We are proud to be backed by the industry leaders

NVIDIA
NVIDIA Inception program

AWS
Cloud infrastructure resources
